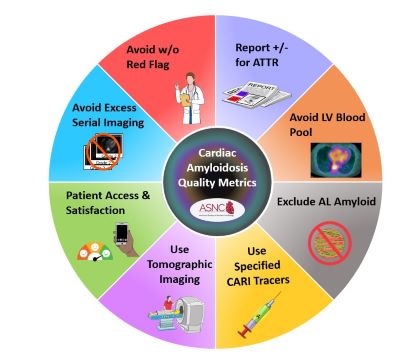
ASNC Publishes Quality Improvement Guide for Nuclear Cardiology Labs Performing Cardiac Amyloidosis Imaging
Includes New Tools for Optimizing Imaging Quality and Improving Patient Care
FAIRFAX, VA (Oct. 28, 2024) – The American Society of Nuclear Cardiology (ASNC) has released a new document defining quality standards for cardiac amyloid radionuclide imaging (CARI) and providing a comprehensive blueprint for assessing and improving imaging quality in the nuclear laboratory. Published online in the Journal of Nuclear Cardiology, ASNC Quality Metrics for Cardiac Amyloid Radionuclide Imaging shows cardiac imagers how to evaluate their labs’ performance against quality standards, identify deficiencies, and introduce quality improvement initiatives with potential to improve the care of patients with cardiac amyloidosis.
CARI is currently the only noninvasive pathway for diagnosing transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis (ATTR-CM). Utilization of CARI has increased significantly in recent years as a result of new data showing the condition is more common than previously believed and the availability of medications that slow or reverse the disease’s progression. Recommendations for CARI indications, protocols, interpretation, and reporting have evolved rapidly over the past decade.
“The bar for quality in cardiac amyloid radionuclide imaging is very high because the results from a single imaging scan can impact the diagnosis and treatment of patients with a devastating disease for the rest of their lives,” says Fadi G. Hage, MD, MASNC, director of nuclear cardiology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, chief of cardiology at the Birmingham VA medical center, and chair of the document’s writing committee. “It is crucial that all labs performing CARI are striving for excellence and have tools to support their efforts.”
This consensus-based document reflects the expertise of 23 leaders in cardiac amyloidosis imaging and the participation of a patient diagnosed with ATTR-CM. The writing group defined quality in CARI across four axes: (1) appropriate indications, (2) patient experience and workflow, (3) instrumentation and protocols, and (4) interpretation and reporting. Each axis is made up of three to four quality metrics that address a current care gap; are measurable, reliable, actionable, and attributable; and have potential to improve patient outcomes. The document guides users, step by step, through the rationale for each metric, how to collect and record data, and cutoff points for good quality vs. excellence. Appendices provide user-friendly templates for data collection within each axis.
ASNC encourages all labs performing CARI to use this new document to assess their performance on the 15 metrics at least annually to allow tracking of progress over time.
“ASNC’s quality measures for CARI provide an excellent opportunity for the entire nuclear cardiology team to work together to create an actionable quality improvement plan customized to their lab and patient population,” says Lawrence Phillips, MD, MASNC, president of ASNC and director of nuclear cardiology at NYU Langone Health. “ASNC’s online resources and guidelines are available to help members and their teams succeed.”
ASNC Quality Metrics for Cardiac Amyloid Radionuclide Imaging is available for download from the Journal of Nuclear Cardiology (JNC).
###
ABOUT ASNC
The American Society of Nuclear Cardiology and its more than 5,200 members have been improving cardiovascular outcomes through image-guided patient management since 1993. As the leading society dedicated solely to the field of nuclear cardiology, ASNC establishes standards for excellence in cardiovascular imaging through the development of clinical guidelines, professional medical education, advocacy and research development. ASNC provides peer-reviewed original articles through its official publication, The Journal of Nuclear Cardiology.
Article Type
Press Release
Category
Guidelines & Quality, Journal of Nuclear Cardiology (JNC), Publications
Related Posts
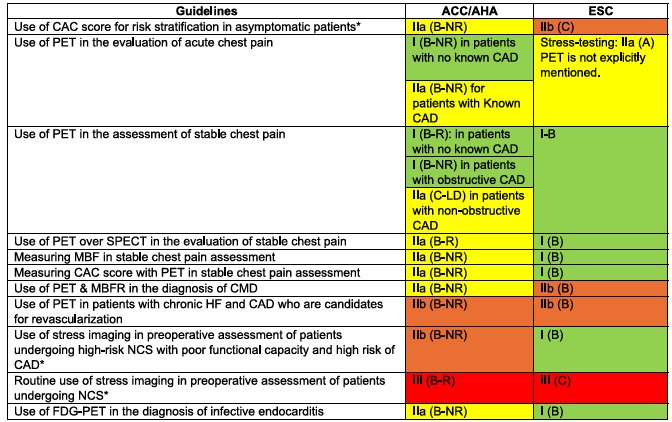
Cardiac PET in the Guidelines: The Update Your Practice Needs Now
Cardiac PET and PET/CT have earned new indications in recently published guidelines…
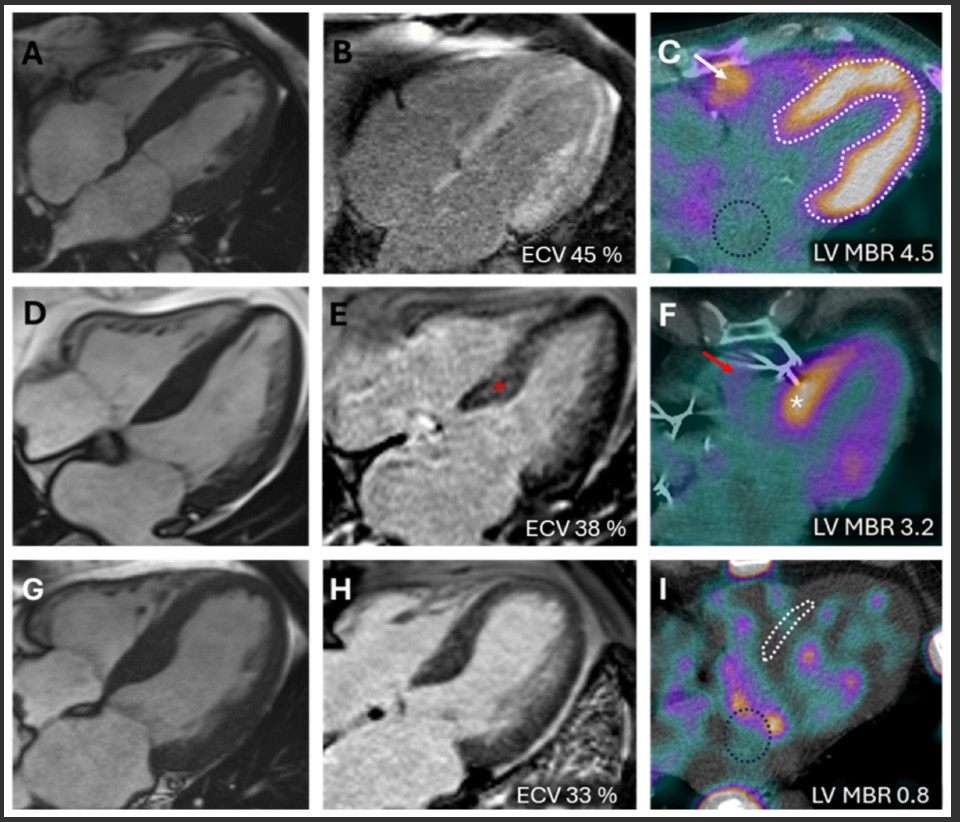
What Is the Next Frontier in Cardiac Amyloidosis Radionuclide Imaging?
The Editor’s Choice study in the May 2025 issue of the Journal…
New Research Suggests Myocardial Flow Reserve Could Transform Risk Stratification
Is a New Risk Scoring Tool on the Horizon? In the new…